Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 25 abril 2025
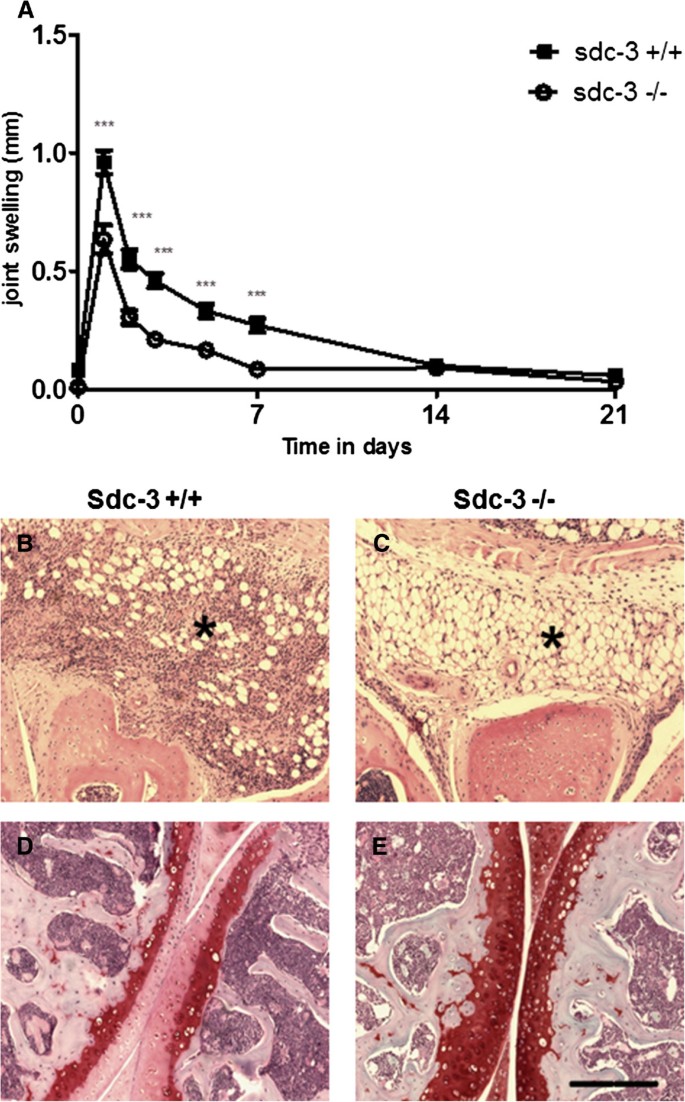
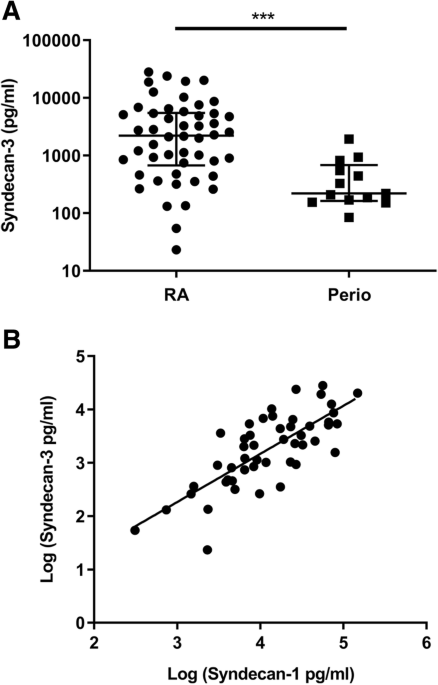
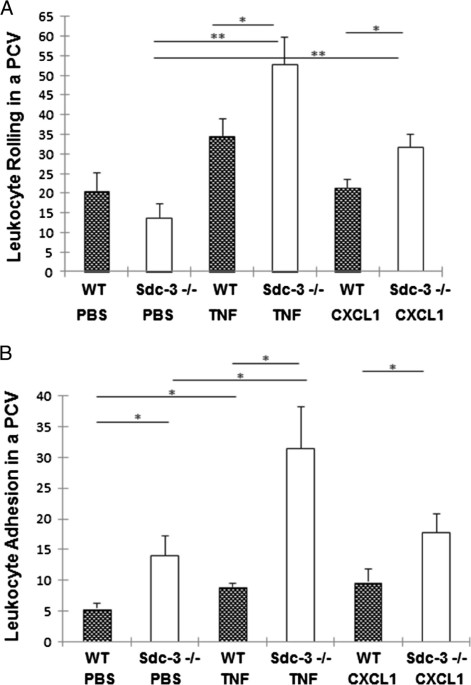
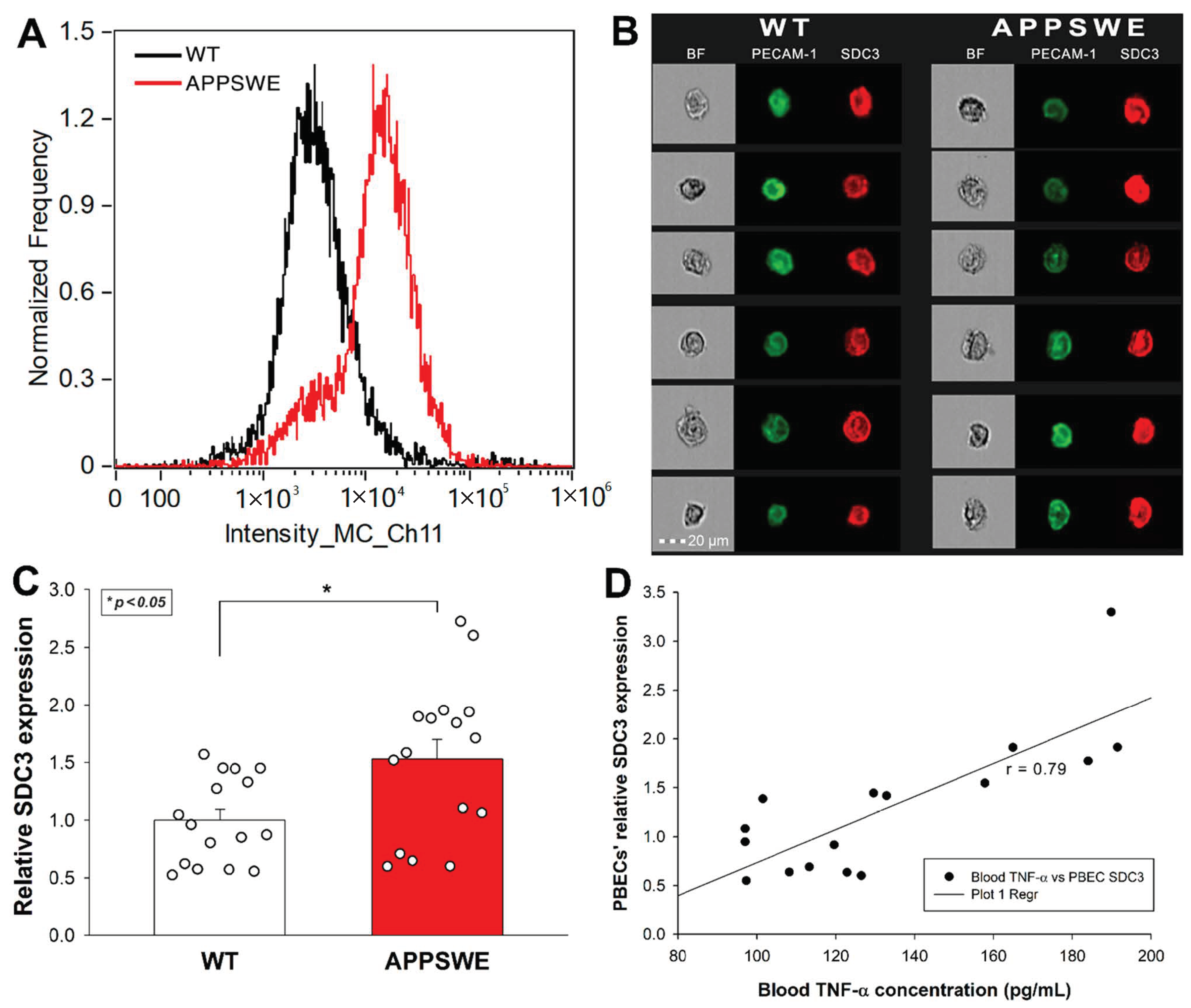
Introduction Syndecans are heparan sulphate proteoglycans expressed by endothelial cells. Syndecan-3 is expressed by synovial endothelial cells of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients where it binds chemokines, suggesting a role in leukocyte trafficking. The objective of the current study was to examine the function of syndecan-3 in joint inflammation by genetic deletion in mice and compare with other tissues. Methods Chemokine C-X-C ligand 1 (CXCL1) was injected in the joints of syndecan-3−/−and wild-type mice and antigen-induced arthritis performed. For comparison chemokine was administered in the skin and cremaster muscle. Intravital microscopy was performed in the cremaster muscle. Results Administration of CXCL1 in knee joints of syndecan-3−/−mice resulted in reduced neutrophil accumulation compared to wild type. This was associated with diminished presence of CXCL1 at the luminal surface of synovial endothelial cells where this chemokine clustered and bound to heparan sulphate. Furthermore, in the arthritis model syndecan-3 deletion led to reduced joint swelling, leukocyte accumulation, cartilage degradation and overall disease severity. Conversely, CXCL1 administration in the skin of syndecan-3 null mice provoked increased neutrophil recruitment and was associated with elevated luminal expression of E-selectin by dermal endothelial cells. Similarly in the cremaster, intravital microscopy showed increased numbers of leukocytes adhering and rolling in venules in syndecan-3−/−mice in response to CXCL1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha. Conclusions This study shows a novel role for syndecan-3 in inflammation. In the joint it is selectively pro-inflammatory, functioning in endothelial chemokine presentation and leukocyte recruitment and cartilage damage in an RA model. Conversely, in skin and cremaster it is anti-inflammatory.
Antirheumatic treatment is associated with reduced serum Syndecan-1 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Soluble syndecan-3 binds chemokines, reduces leukocyte migration in vitro and ameliorates disease severity in models of rheumatoid arthritis, Arthritis Research & Therapy
Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy
IJMS, Free Full-Text
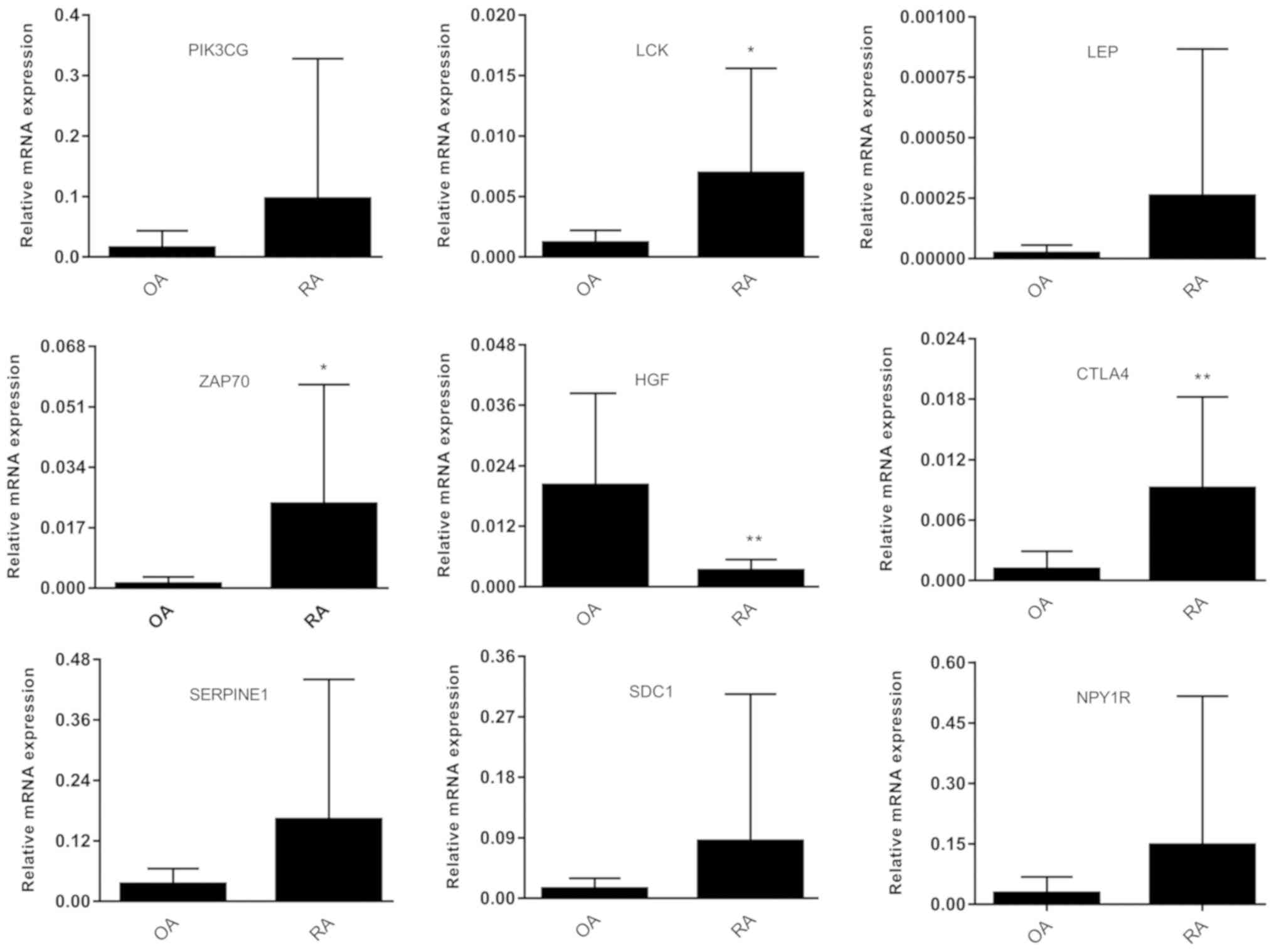
Identification of pivotal genes and pathways in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis through integrated bioinformatic analysis

Synovial fibroblasts as potential drug targets in rheumatoid arthritis, where do we stand and where shall we go?

Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived matrikines in osteoarthritis
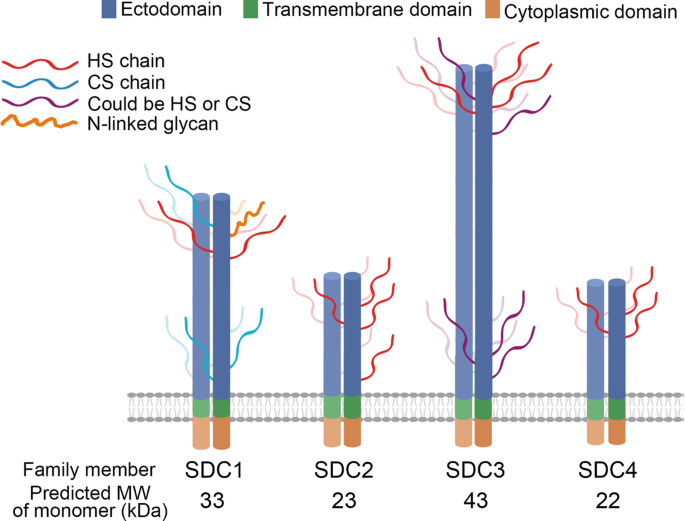
Syndecan-3: A Signaling Conductor in the Musculoskeletal System

Proteome Profiler Human Cytokine Array Kit ARY005B: R&D Systems

PDF) An approach to the analysis of gene expression in chronically activated T Lymphocytes

Secondary structure prediction of syndecan-3 core protein. N-terminal

Synovial fibroblasts assume distinct functional identities and secrete R-spondin 2 to drive osteoarthritis












/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/g/H/QErBUUQ2uGyb5Rdgnqqg/techtudo.png)