Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 17 março 2025
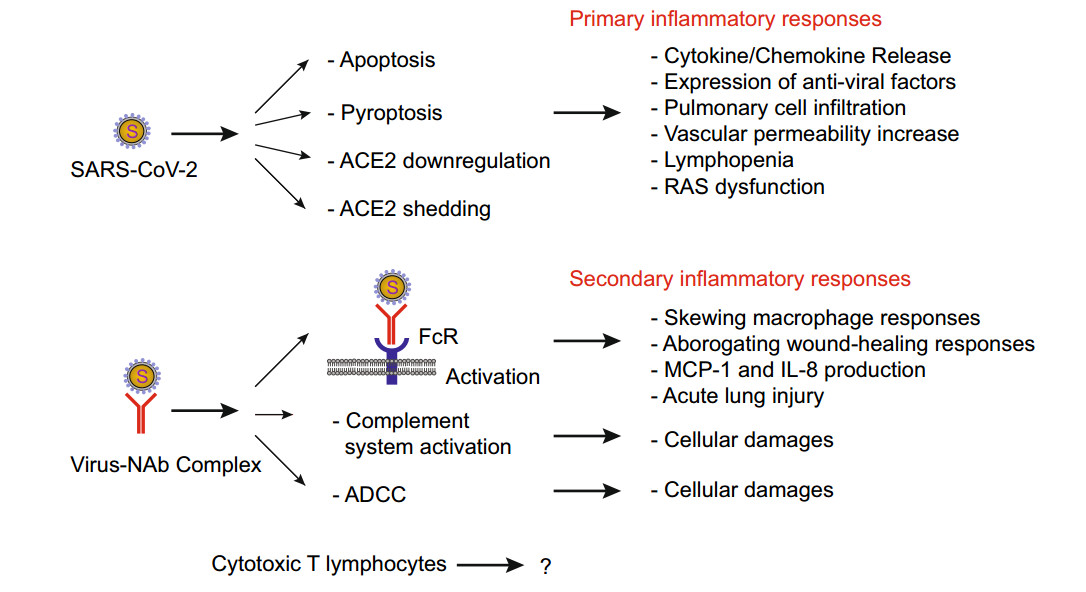
Currently there is no effective antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection, which frequently leads to fatal inflammatory responses and acute lung injury. Here, we discuss the various mechanisms of SARS-CoV-mediated inflammation. We also assume that SARS-CoV-2 likely shares similar inflammatory responses. Potential therapeutic tools to reduce SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory responses include various methods to block FcR activation. In the absence of a proven clinical FcR blocker, the use of intravenous immunoglobulin to block FcR activation may be a viable option for the urgent treatment of pulmonary inflammation to prevent severe lung injury. Such treatment may also be combined with systemic anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. However, these strategies, as proposed here, remain to be clinically tested for effectiveness.

Defining the features and duration of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with disease severity and outcome

Physical activity and anti-inflammatory response in SARS-CoV2

Autoimmunity and Inflammation

Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools

Study reveals how young children's immune systems tame SARS-CoV-2
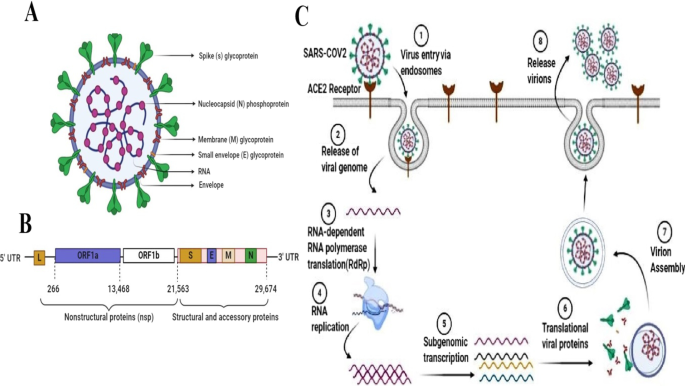
Understanding the pivotal roles of ACE2 in SARS-CoV-2 infection: from structure/function to therapeutic implication, Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics

Innate immunological pathways in COVID-19 pathogenesis
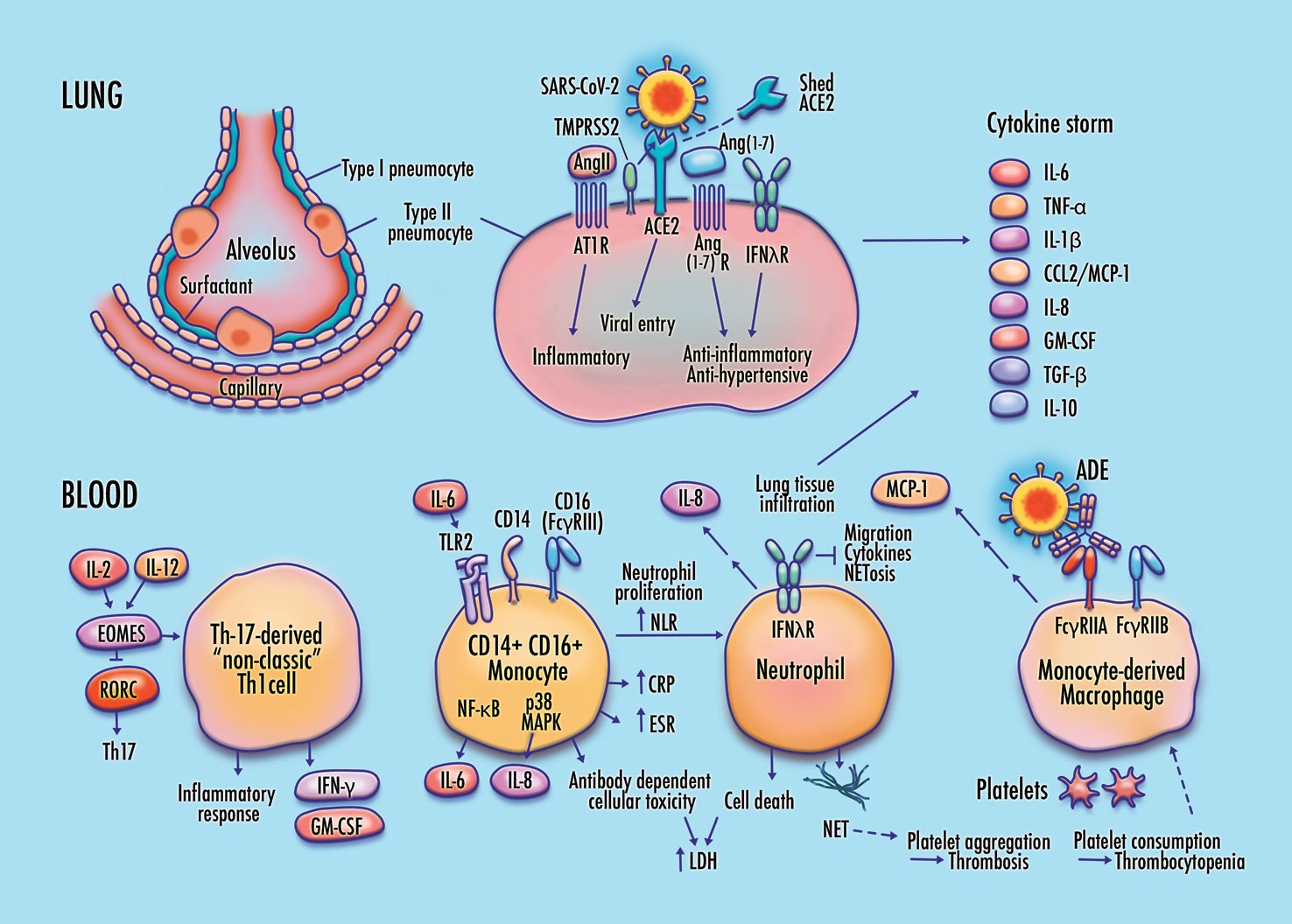
Frontiers Cellular and Molecular Pathways of COVID-19 and Potential Points of Therapeutic Intervention
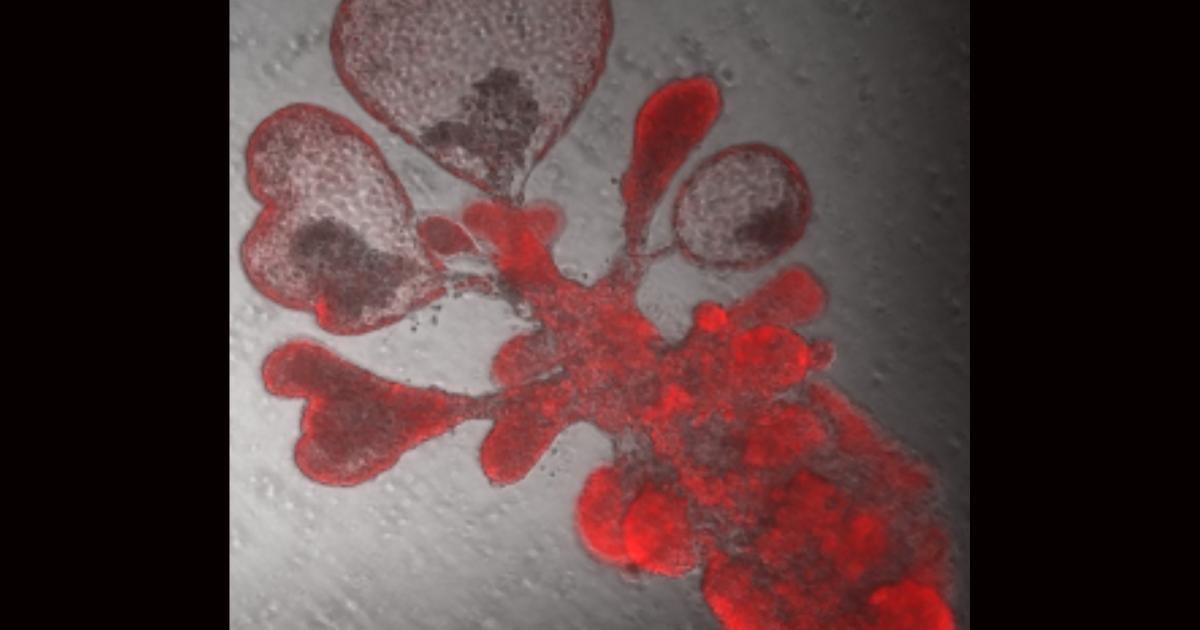
Lab-Grown Mini-Lungs Mimic the Real Thing – Right Down to Covid Infection
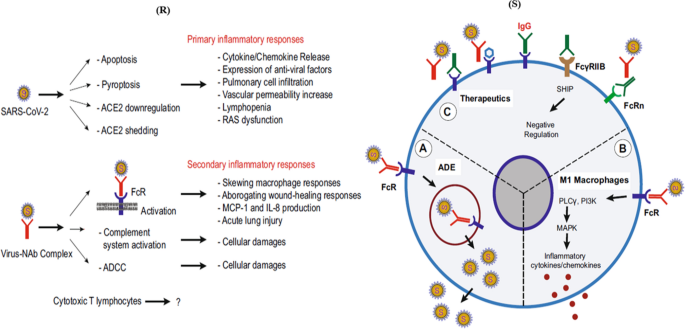
COVID-19: inflammatory responses, structure-based drug design and potential therapeutics
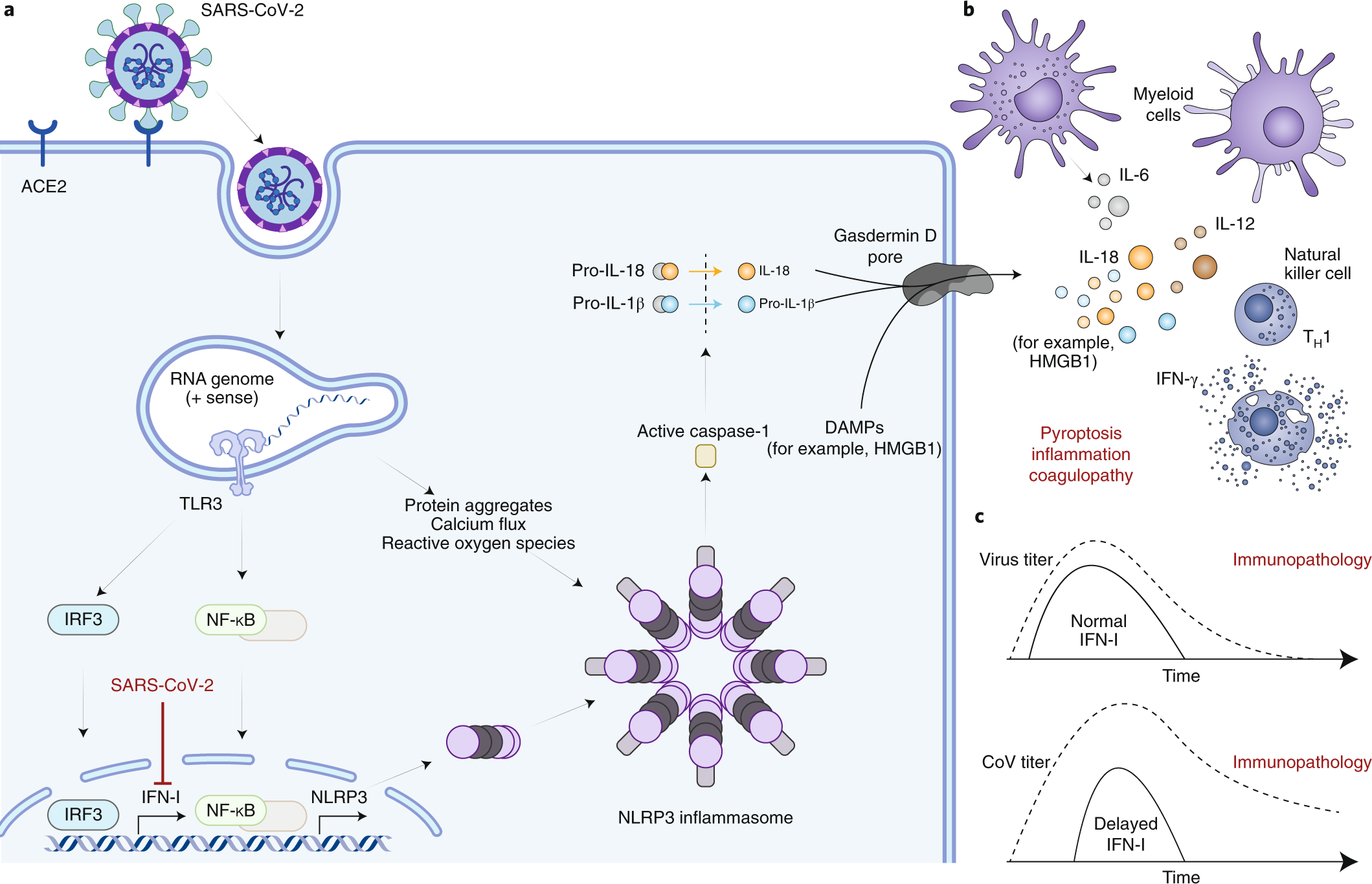
Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity
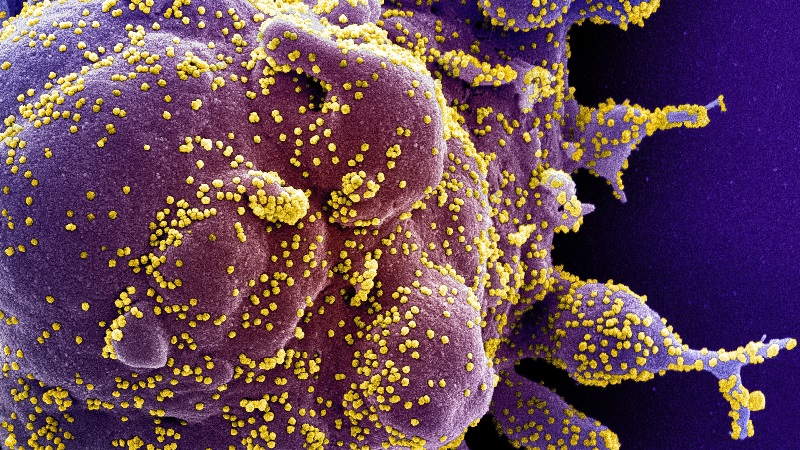
Blocking Immune System Pathway May Stop COVID-19 Infection, Prevent Severe Organ Damage

COVID-19