Deep Learning-Based Real-Time AI Virtual Mouse System Using Computer Vision to Avoid COVID-19 Spread
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 abril 2025

The mouse is one of the wonderful inventions of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) technology. Currently, wireless mouse or a Bluetooth mouse still uses devices and is not free of devices completely since it uses a battery for power and a dongle to connect it to the PC. In the proposed AI virtual mouse system, this limitation can be overcome by employing webcam or a built-in camera for capturing of hand gestures and hand tip detection using computer vision. The algorithm used in the system makes use of the machine learning algorithm. Based on the hand gestures, the computer can be controlled virtually and can perform left click, right click, scrolling functions, and computer cursor function without the use of the physical mouse. The algorithm is based on deep learning for detecting the hands. Hence, the proposed system will avoid COVID-19 spread by eliminating the human intervention and dependency of devices to control the computer.
Google Research: Looking Back at 2020, and Forward to 2021 – Google Research Blog

PDF) Deep Learning-Based Real-Time AI Virtual Mouse System Using Computer Vision to Avoid COVID-19 Spread

Deep Learning-Based Real-Time AI Virtual Mouse System Using Computer Vision to Avoid COVID-19 Spread. - Abstract - Europe PMC
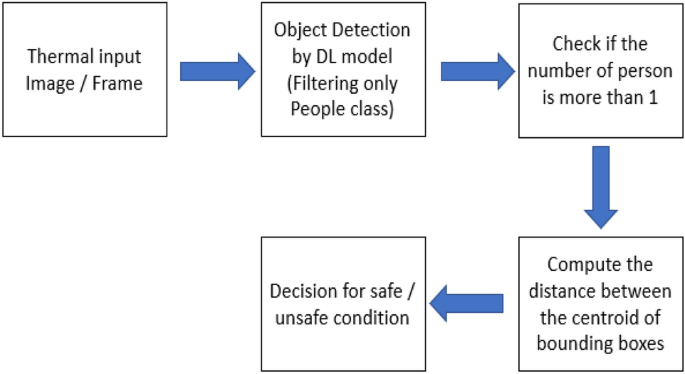
Implementing a real-time, AI-based, people detection and social distancing measuring system for Covid-19

PDF] Deep Learning-Based Real-Time AI Virtual Mouse System Using Computer Vision to Avoid COVID-19 Spread

Flowchart of The Methods of Gesture Based Mouse
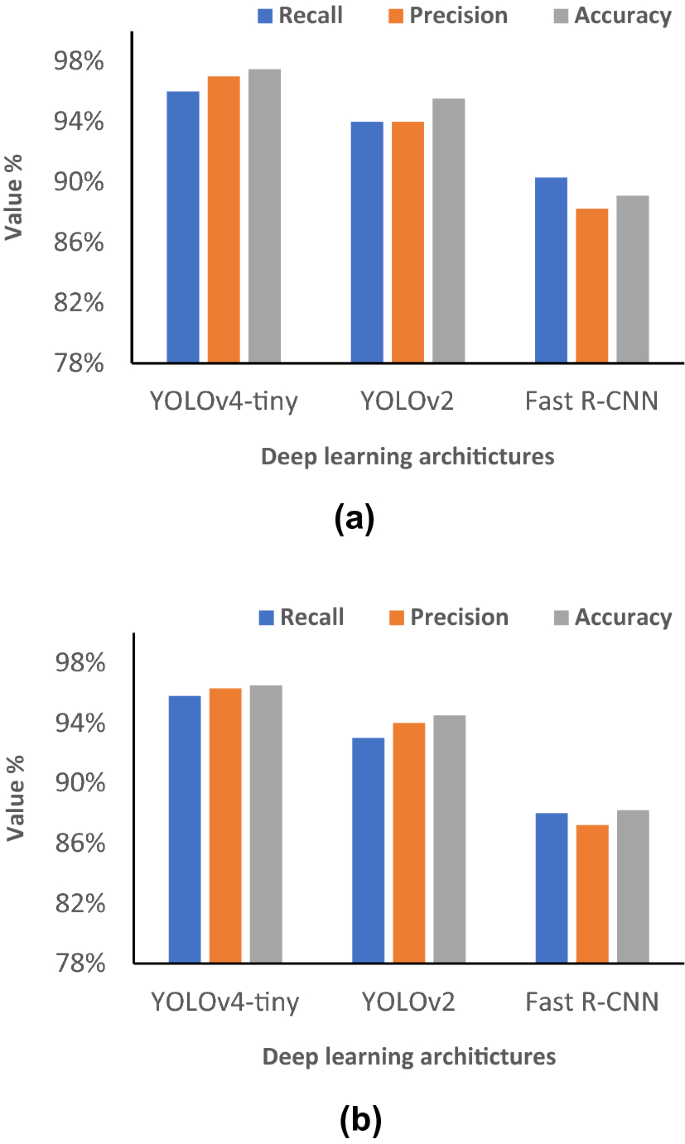
Developing a real-time social distancing detection system based on YOLOv4-tiny and bird-eye view for COVID-19
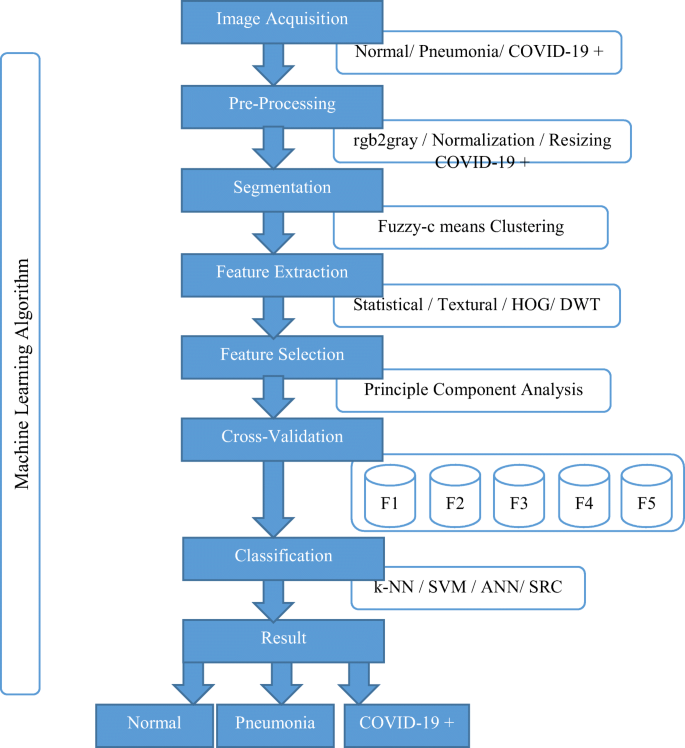
Machine learning-based automatic detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease
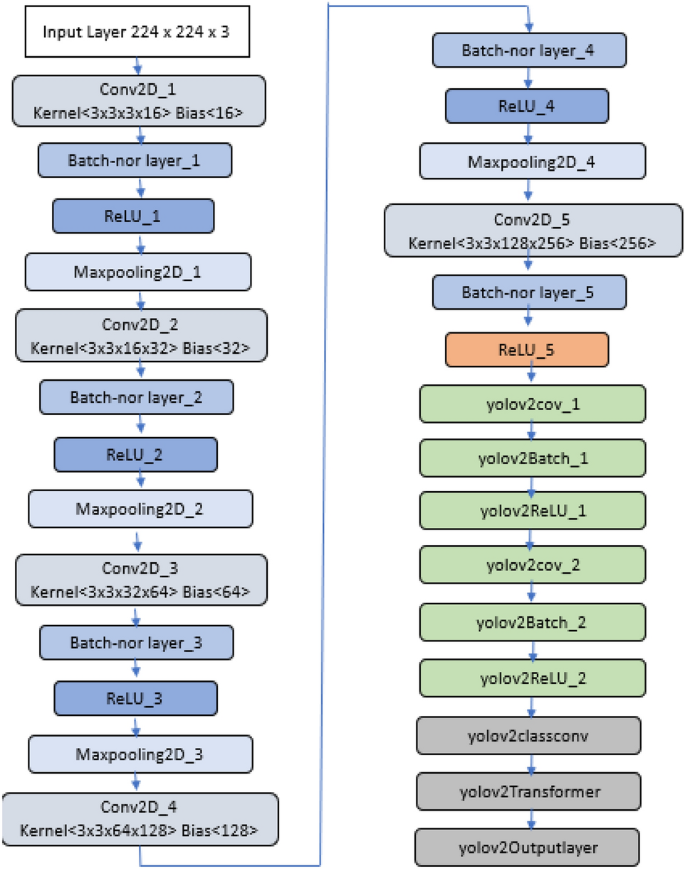
Implementing a real-time, AI-based, people detection and social distancing measuring system for Covid-19
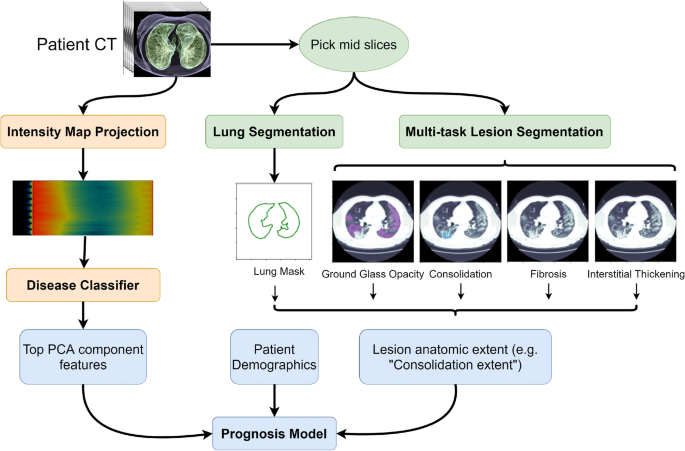
Effective deep learning approaches for predicting COVID-19 outcomes from chest computed tomography volumes