Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 24 fevereiro 2025
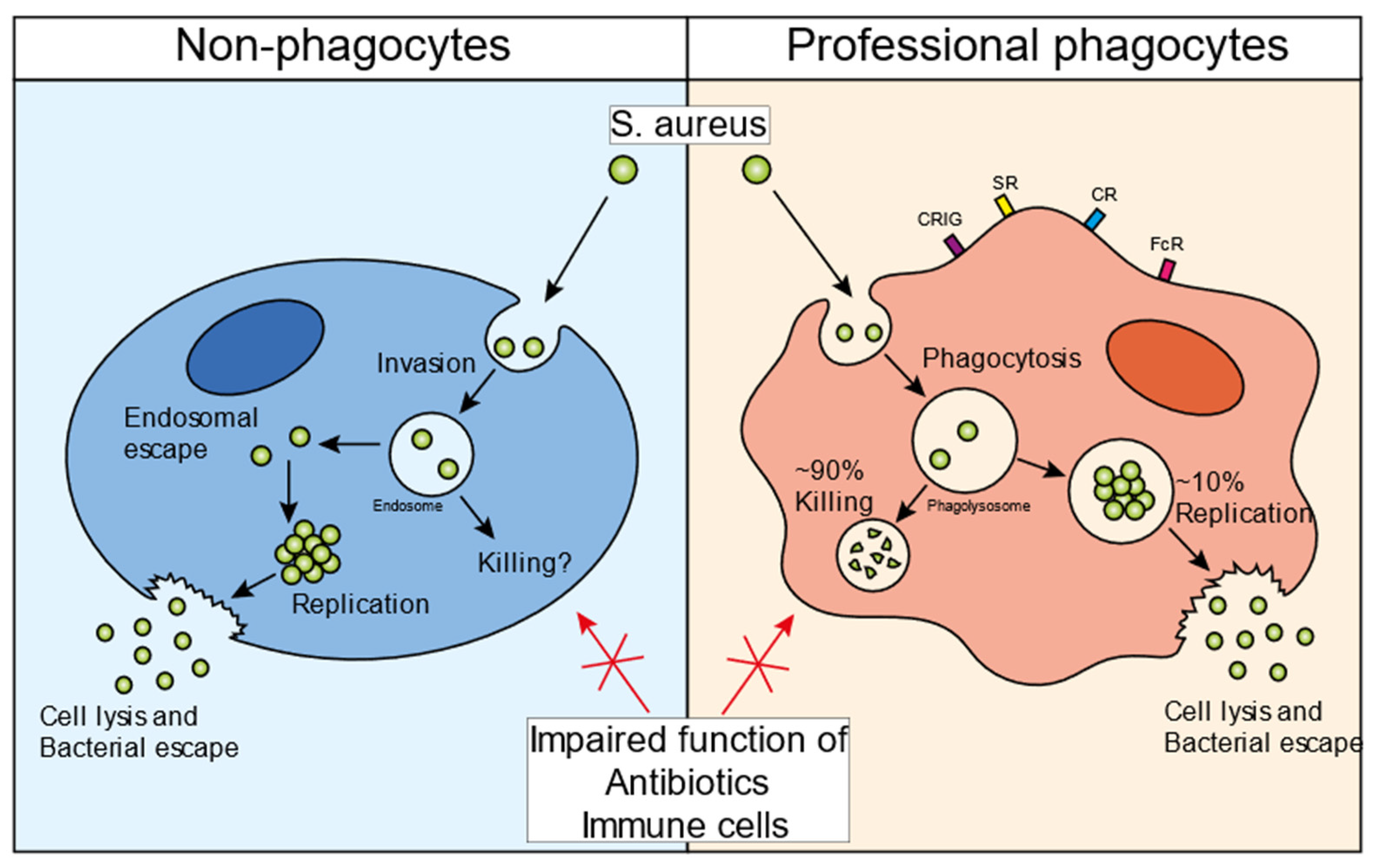
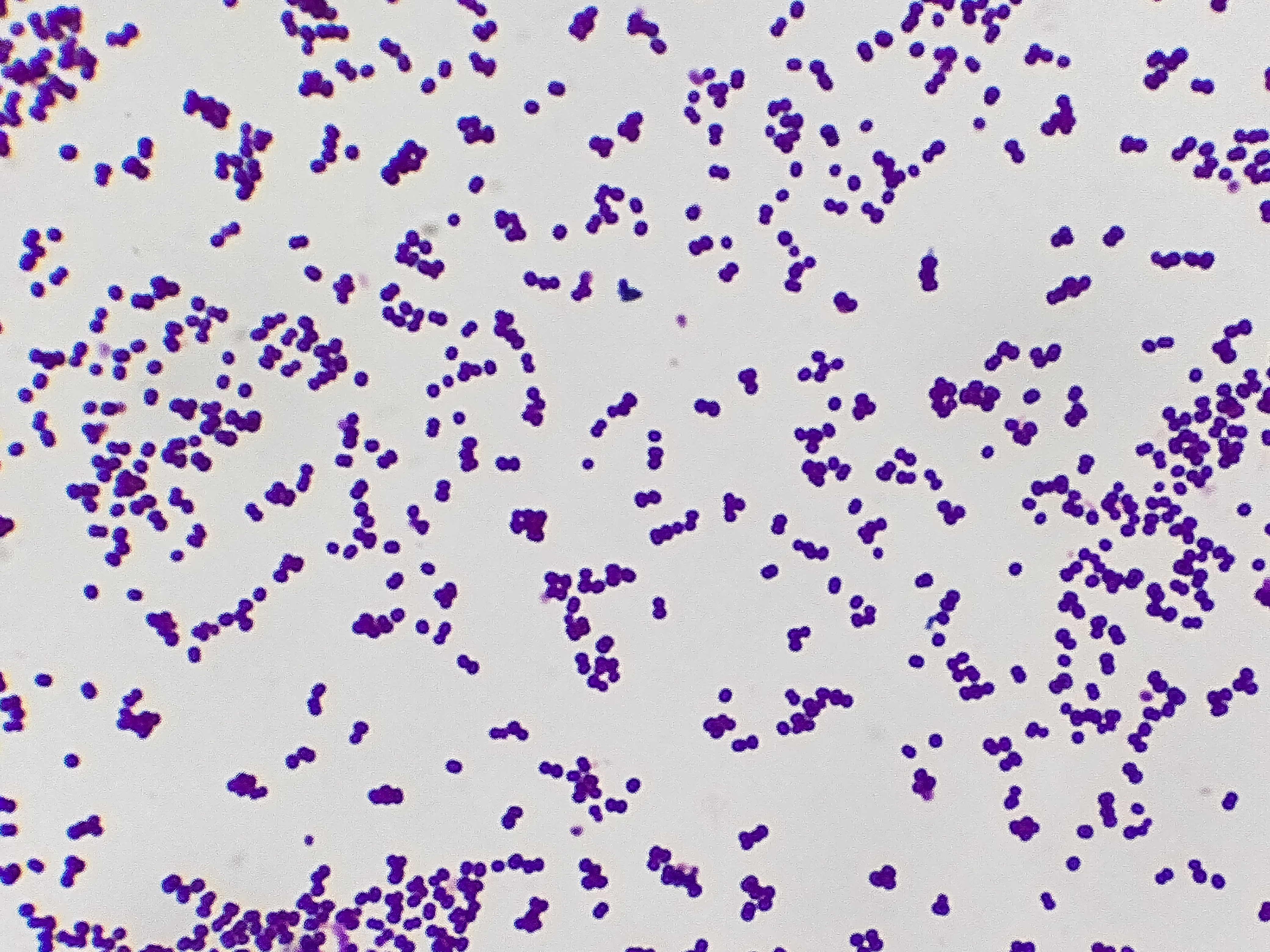
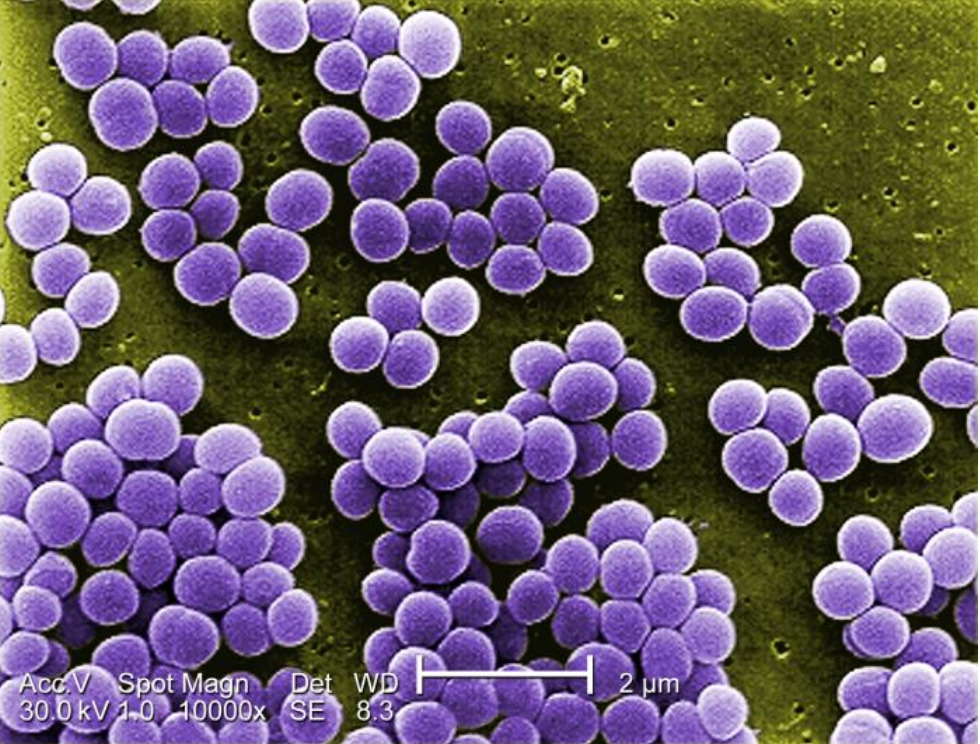
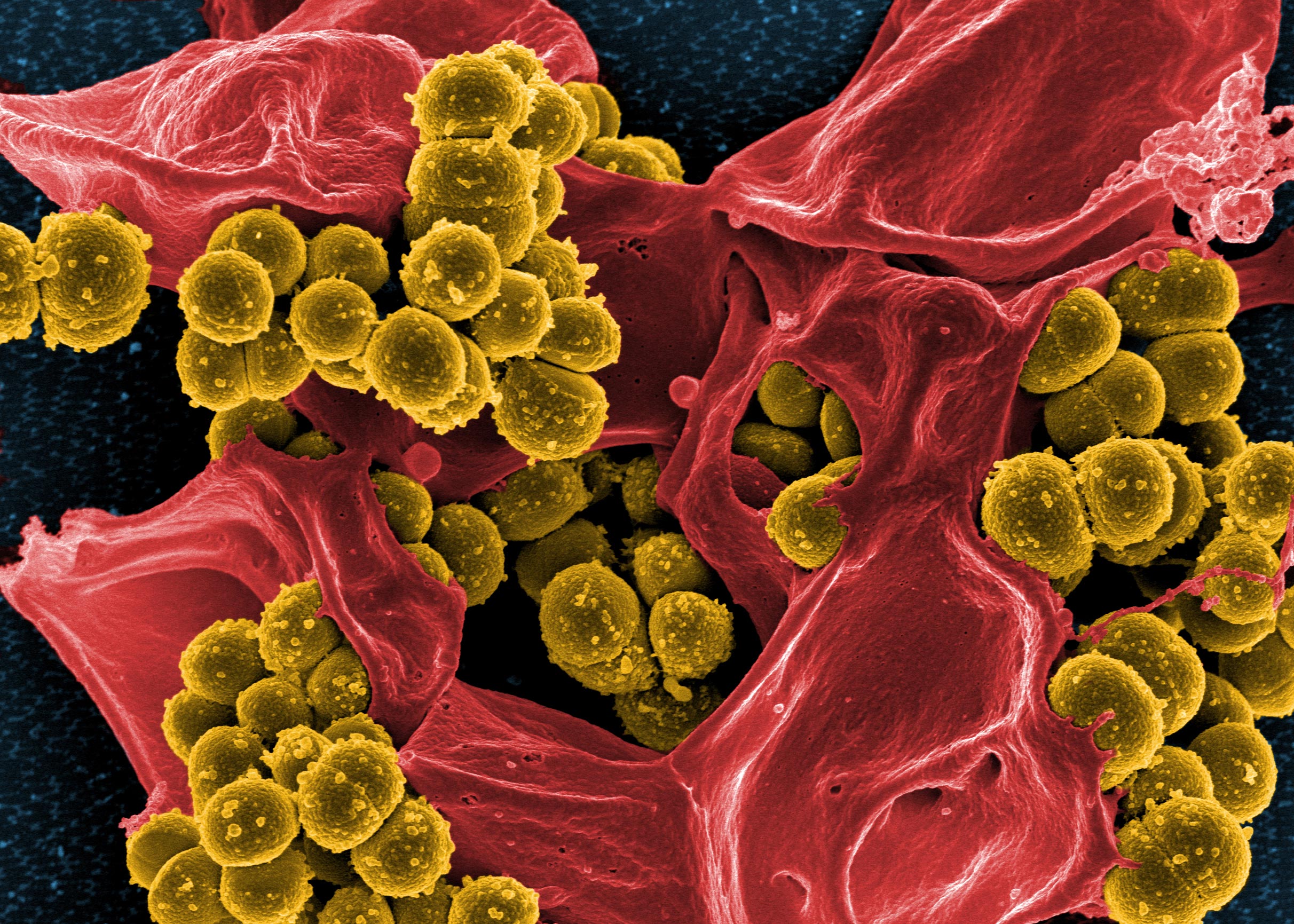
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections pose a global health threat, especially with the continuous development of antibiotic resistance. As an opportunistic pathogen, MRSA infections have a high mortality rate worldwide. Although classically described as an extracellular pathogen, many studies have shown over the past decades that MRSA also has an intracellular aspect to its infectious cycle, which has been observed in vitro in both non-professional as well as professional phagocytes. In vivo, MRSA has been shown to establish an intracellular niche in liver Kupffer cells upon bloodstream infection. The staphylococci have evolved various evasion strategies to survive the antimicrobial environment of phagolysosomes and use these compartments to hide from immune cells and antibiotics. Ultimately, the host cells get overwhelmed by replicating bacteria, leading to cell lysis and bacterial dissemination. In this review, we describe the different intracellular aspects of MRSA infection and briefly mention S. aureus evasion strategies. We discuss how this intracellular niche of bacteria may assist in antibiotic tolerance development, and lastly, we describe various new antibacterial strategies that target the intracellular bacterial niche.

The Ageless Generation: How Advances in Biomedicine Will Transform

Critical Sequence Hotspots for Binding of Novel Coronavirus to

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Full article: Molecular basis of the potential interaction of SARS

Collaboration with Generate Biomedicines
Psp Iso Tool 1.91 Download - Colaboratory

3-[(1S,2S,3R)-2,3-Difluoro-1-hydroxy-7-methylsulfonylindan-4-yl







![Pokémon the Series: XYZ Set 2 [DVD] : Various, Various](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/W/MEDIAX_792452-T2/images/I/81z+HU0zV9L._AC_UF350,350_QL80_.jpg)